Mature Functions: Programmed Ferroptosis
1 Preprocessing
The default GEO data file is located at C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429.
Change the working directory in R to: C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429.
Highly recommended to use Rstudio. Need to select the environment which containing anndata, in Tools > Global options > Python > Python interpreter
1.1 Load required packages (R Studio)
library(DEsingle)
library(Seurat)
library(multtest)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(patchwork)
library(tidyverse)
library(future)
library(RColorBrewer)
library(SummarizedExperiment)
library(scater)
library(cowplot)
library(harmony)
library(monocle3)
library(uwot)
library(ComplexHeatmap)
library(ggrepel)
1.2 Create vector to read files (R)
#Database download link: https://biocomputing.cowtransfer.com/s/2df0081e282147
#Password: ufurmd
setwd("C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429")
#File Structure
# ---[C:\]
# ---[GEOANALYSIS]
# ---[GSE232429]
# ---[Sham1]
# ---matrix.mtx.gz
# ---features.tsv.gz
# ---barcodes.tsv.gz
# ---[MCAO1]
# ---matrix.mtx.gz
# ---features.tsv.gz
# ---barcodes.tsv.gz
# ---[MCAO2]
# ---matrix.mtx.gz
# ---features.tsv.gz
# ---barcodes.tsv.gz
1.3 Read data (R)
Sham1<- Read10X(data.dir = "Sham1")
MCAO1<- Read10X(data.dir = "MCAO1")
MCAO2<- Read10X(data.dir = "MCAO2")
1.4 Create Seurat object and filter. Add code to filter out cells with fewer than 200 genes (min.features = 200) and genes covered by fewer than 3 cells (min.cells = 3) (R)
Sham1<- CreateSeuratObject(counts =Sham1, project = "Sham1", min.features = 200, min.cells = 3)
MCAO1<- CreateSeuratObject(counts =MCAO1, project = "MCAO1", min.features = 200, min.cells = 3)
MCAO2<- CreateSeuratObject(counts =MCAO2, project = "MCAO2", min.features = 200, min.cells = 3)
# Calculate mitochondrial DNA
Sham1[["percent.mt"]] <- PercentageFeatureSet(Sham1, pattern = "^mt-")
MCAO1[["percent.mt"]] <- PercentageFeatureSet(MCAO1, pattern = "^mt-")
MCAO2[["percent.mt"]] <- PercentageFeatureSet(MCAO2, pattern = "^mt-")
# Merge data and plot quality control (QC)
CI <- merge(Sham1, y=c(MCAO1, MCAO2), add.cell.ids = c("Sham1", "MCAO1", "MCAO2"), project = "all")
head(colnames(CI))
unique(sapply(X = strsplit(colnames(CI), split = "_"), FUN = "[", 1))
plot1 <- FeatureScatter(CI, feature1 = "nFeature_RNA", feature2 = "percent.mt")
plot2 <- FeatureScatter(CI, feature1 = "nCount_RNA", feature2 = "nFeature_RNA")
CombinePlots(plots = list(plot1, plot2))#Quality control plot1
VlnPlot(CI, features = c("percent.mt", "nFeature_RNA", "nCount_RNA"), ncol = 3, pt.size=0)#Quality control plot2
VlnPlot(CI, features = c("percent.mt", "nFeature_RNA", "nCount_RNA"), ncol = 3, pt.size=0.5)#Quality control plot3
1.5 Remove cells with high mitochondrial gene expression or extreme values (R)
# Parameters referenced from https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/2195816 and https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/484804392
# nFeature_RNA: Genes expressed in each cell > 300 and < 7000;
# mt_percent: Mitochondrial gene expression < 25% of total gene expression;
Sham1<- subset(Sham1, subset = nFeature_RNA > 300 & nFeature_RNA < 7000 &
percent.mt < 25)
MCAO1<- subset(MCAO1,subset = nFeature_RNA > 300 & nFeature_RNA < 7000 &
percent.mt < 25)
MCAO2<- subset(MCAO2, subset = nFeature_RNA > 300 & nFeature_RNA < 7000 &
percent.mt < 25)
1.6 Perform CCA integration (R)
myfunction1 <- function(testA.seu){
testA.seu <- NormalizeData(testA.seu, normalization.method = "LogNormalize", scale.factor = 10000)
testA.seu <- FindVariableFeatures(testA.seu, selection.method = "vst", nfeatures = 2000)
return(testA.seu)
}
Sham1<- myfunction1(Sham1)
MCAO1<- myfunction1(MCAO1)
MCAO2<- myfunction1(MCAO2)
1.7 Integration (R)
list <- list (Sham1, MCAO1, MCAO2)
testAB.anchors <- FindIntegrationAnchors(object.list = list, dims = 1:20)
testAB.integrated <- IntegrateData(anchorset = testAB.anchors, dims = 1:20)
1.8 Add sample and group information (R)
# Retrieve metadata
metadata <- testAB.integrated@meta.data
# Copy 'orig.ident' to new column 'Sample'
metadata$Sample <- metadata$orig.ident
# Create new column 'Group' based on 'orig.ident'
metadata$Group <- ifelse(grepl("Sham", metadata$orig.ident), "Sham",
ifelse(grepl("MCAO", metadata$orig.ident), "MCAO", NA))
# Ensure updated metadata is reassigned to Seurat object
testAB.integrated@meta.data <- metadata
# Check results
head(testAB.integrated@meta.data)
1.9 As per documentation, use ‘integrated’ for finding cluster markers and ‘RNA’ (normalized data) for differential analysis (R)
# Set default matrix to 'integrated' for subsequent steps
DefaultAssay(testAB.integrated) <- "integrated"
# Run the standard workflow for visualization and clustering
testAB.integrated <- ScaleData(testAB.integrated, features = rownames(testAB.integrated))
testAB.integrated <- RunPCA(testAB.integrated, npcs = 50, verbose = FALSE)
testAB.integrated <- FindNeighbors(testAB.integrated, dims = 1:30)
testAB.integrated <- FindClusters(testAB.integrated, resolution = 0.1)
testAB.integrated <- RunUMAP(testAB.integrated, dims = 1:10)
testAB.integrated <- RunTSNE(testAB.integrated, dims = 1:30)
save(testAB.integrated, file = "GSE232429 Neuron.Rdata")
1.10 Save the file as h5ad for further analysis in Python (R)
library(SeuratDisk)
convert_Rdata_to_H5AD <- function(rdata_path) {
file_dir <- dirname(rdata_path)
file_name <- tools::file_path_sans_ext(basename(rdata_path))
load(rdata_path)
object_names <- ls()
# 检查是否为 Seurat 对象
for (obj_name in object_names) {
obj <- get(obj_name)
if (inherits(obj, "Seurat")) {
# 保存为 H5Seurat 格式
h5seurat_path <- file.path(file_dir, paste0(file_name, "_", obj_name, ".h5Seurat"))
SaveH5Seurat(obj, filename = h5seurat_path)
# 转换为 H5AD 格式
h5ad_path <- file.path(file_dir, paste0(file_name, "_", obj_name, ".h5ad"))
Convert(h5seurat_path, dest = "h5ad")
cat("Conversion complete for object", obj_name, ". H5AD file saved at:", h5ad_path, "/n")
}
}
}
#Export H5AD Files
# args <- commandArgs(trailingOnly = TRUE)
args <- "GSE232429 Neuron.Rdata"#工作路径下的Rdata文件
if (length(args) == 0) {
stop("No .Rdata file path provided. Usage: Rscript script_name.R <path_to_Rdata>")
}
rdata_path <- args[1]
convert_Rdata_to_H5AD(rdata_path)
H5ad saved as GSE232429 Neuron_testAB.integrated.h5ad. Because the automatically generated file name is too long, change it to GSE232429 Neuron.h5ad
Save the variable table as Round0.Rdata. OR: Do not close R to ensure the subsequent programs can run.
Round 1
2 𝙄𝙙𝙚𝙣𝙩𝙞𝙛𝙮 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡𝙨 𝙪𝙣𝙙𝙚𝙧𝙜𝙤𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙥𝙧𝙤𝙜𝙧𝙖𝙢𝙢𝙚𝙙 𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙧𝙤𝙥𝙩𝙤𝙨𝙞𝙨.
Start
2.1 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟏: 𝐀𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐚𝐭𝐞 𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐱𝐢𝐦𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐦𝐞𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐝. (Python)
Import GSE232429 Neuron.h5ad into [LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis\data\.
import numpy as np
import os
import LittleSnowFox as kl
print(kl.__version__)
kl.kl_initialize(0)
parent_directory_origin = kl.kl_settings.parent_directory_origin
print(parent_directory_origin)
current_folder = kl.workcatalogue.choosemode_kl(parent_directory_origin,'Lineage',1)
print(current_folder)
current_folder = kl.workcatalogue.choosemode_kl(parent_directory_origin,'Lineage',1)
print(current_folder)
#选择要使用哪个样本
choosen_sample = "Nerveferroptosis"
#选择.h5ad文件
h5ad_filename = "GSE232429 Neuron.h5ad"
#运行自带的示例,并获取稀疏矩阵
#这里需要做非示例的函数进去
current_folder_input = current_folder
orig_adata,loading_directory,distance_matrix = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix_sample(
choosen_sample,
h5ad_filename,
"draw",
current_folder_input,
round_of_smooth=1,
neighbor_N=13000,
beta=0.1,
truncation_threshold=0.001,
save_subset=True,
use_existing_KNN_graph=False,
compute_new_Smatrix=True,
use_full_Smatrix = True,
)
#orig_adata,loading_directory,distance_matrix_sparse = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix_sample(choosen_sample,h5ad_filename,"draw",current_folder_input)
#运行自带的示例,并获取非稀疏矩阵
#这里需要做非示例的函数进去
#current_folder_input = current_folder
#loading_directory,distance_matrix = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix(choosen_sample,h5ad_filename,"draw",current_folder_input)
orig_adata.obs['orig.ident']
orig_adata
#需要区分dense和sparase
save_list = ["orig_adata.obs['orig.ident']", "orig_adata.obsm['X_umap']"]
import scipy.sparse
distance_matrix_sparse = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix(distance_matrix)
#将要计算的文件保存到/result
merged_csv,result_directory = kl.workcatalogue.kl_save(loading_directory,choosen_sample,distance_matrix_sparse,save_list,orig_adata)
2.2 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟐: 𝐔𝐬𝐞 𝐮𝐧𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐧𝐢𝐧𝐠. (Matlab)
Afterward, execute the following file:
[LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis\main_v3_matlab_run_me.m
%% Load data and Split to compute
%% Load data and Split to compute
MM0 = load('./result/distance_matrix.mat');
MM0 = MM0.distance_matrix;
MM0=full(MM0);
%% 读取要排序的对象
count_=readtable('./result/merged_data.csv');
%% 得到边界划分点
[p,splitlist] = binary_corr_sorting(MM0,20,500,5,5);
%% 对划分点去重
[uniqueList, ~, ~] = unique(splitlist, 'stable');
%% 对相似度矩阵排序
MM=MM0(p,p);
split=[];
%% 重排count_result
count_result=count_(p,:);
split_simple=uniqueList;
%% 第一个起始位点置为1
split_simple(1)=1;
split_simple=[split_simple,length(MM0)];
%% 计算均值矩阵
[simple_matrix]=sample_computing(count_result,split_simple,MM,"mean");
%% 合并成小矩阵
ClusterReslut=cluster_map(split_simple,simple_matrix,0,0.0002,0);
count_result.Result = ClusterReslut;
%重排小矩阵
[cluster_map_matrix] = genetic_encoder( ...
simple_matrix, ...
60, ...% nPop = 50; % 种群规模大小为30
1, ...% nPc = 1; % 子代规模的比例0.8
200, ...% maxIt = 200; % 最大迭代次数
5 ...% cycletimes = 200; % 循环计算次数
);
%重拍小矩阵方案2
% 创建行和列标签(示例)
%row_labels = cluster_map_label;
%column_labels = cluster_map_label;
% 使用 heatmap 函数并传递相应参数
h = heatmap(cluster_map_matrix);
%h.YDisplayLabels = row_labels; % 设置行标签
%h.XDisplayLabels = column_labels; % 设置列标签
h.ColorLimits = [0, 0.00007]
% %对小矩阵进行排序
% %计算pesudotime,两种计算模式,mean和median
% %疑问,pseudotime跟着小矩阵重排了吗?
% [pesudotime_info] = pesudotime_combine(split_simple,count_.Pst,"mean")
% %使用sigmoid函数处理伪时间
% pesudotime_info_sigmoid = sigmoid(pesudotime_info,45,10,100);
% %pesudotime_info_sigmoid = pesudotime_info;
% % 使用 heatmap 函数并传递相应参数
%
% number_of_length = 1:length(cluster_map_matrix);
%
% row_labels = pesudotime_info_sigmoid;
% column_labels = number_of_length;
figure(1)
hi = heatmap(cluster_map_matrix);
hi.ColorLimits = [0, 0.00002]
hi.YDisplayLabels = row_labels; % 设置行标签
hi.XDisplayLabels = column_labels; % 设置列标签
%% 临近法激活
%临近法激活,()
corr_matrix = relevance_generate(0.00007,3,cluster_map_matrix);
heatmap(corr_matrix);
%% 编码
encode_result = encoder_corr_matrix(0.000071,0.000069,50,3,cluster_map_matrix);
figure(2)
hj = heatmap(encode_result);
%% 解码
figure(3)
[weighting_decode,decode_result] = decoder_corr_matrix(encode_result);
weighting_result = weighting_decode + decode_result;
hk = heatmap(weighting_result);
hk.ColorLimits = [40, 50]
writetable(count_result,"result/1n13000_result.csv");
Group result generated in [LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis\result\1n13000_result.csv.
2.3 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟑: 𝐏𝐞𝐫𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦 𝐨𝐦𝐢𝐜𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐬. (R)
Open variable table Round0.Rdata to continue. OR: You didn’t closed R Studio.
2.3.1 After analysis, import results from ‘1n13000_result.csv’ into metadata (R)
Place 1n13000_result.csv in the R working directory. File is usuallly located at C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429/
load("C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429/GSE232429 Neuron.Rdata")
# Read CSV file
result_data <- read.csv("1n13000_result.csv", stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
# Ensure the file contains columns 'Var1' and 'Result'; check file content
head(result_data)
# Check if all 'Var1' values exist in Seurat object's cell names
common_cells <- intersect(result_data$Var1, rownames(testAB.integrated@meta.data))
if (length(common_cells) < nrow(result_data)) {
warning("Some cells in '1n13000_result.csv' are not found in testAB.integrated metadata!")
}
# Map 'Result' values to Seurat object's metadata based on 'Var1'
# First, create a new column 'Result' and set it to NA
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Result <- NA
# Use match() to merge corresponding values
matching_indices <- match(rownames(testAB.integrated@meta.data), result_data$Var1)
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Result <- result_data$Result[matching_indices]
## Group based on 'Result'
# 获取 metadata
metadata <- testAB.integrated@meta.data
# Create new column 'ranse' based on 'Result' values
metadata$ranse <- with(metadata,
ifelse(Result >= 1 & Result <= 10, "Group R1-1",
ifelse(Result >= 11 & Result <= 18, "Group R1-2",
ifelse(Result >= 19 & Result <= 29, "Group R1-3",
ifelse(Result >= 30 & Result <= 39, "Group R1-4",
ifelse(Result >= 40 & Result <= 68, "Group R1-5", NA))))))
# Construct 'Biaoqian' column by removing 'Group ' from 'ranse'
metadata$Biaoqian <- gsub("^Group ", "", metadata$ranse)
# Assign updated metadata back to the Seurat object
testAB.integrated@meta.data <- metadata
# Check results
head(testAB.integrated@meta.data)
2.3.2 Visualization (R)
cell_type_cols <- c("#6693b1","#a3caa9","#deedad","#dd9667","#bd5c56")
p1 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "ranse", split.by = "Group", pt.size=0.5, label = T, repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 3A-1.pdf", plot = p1, device = 'pdf', width = 26, height = 14, units = 'cm')
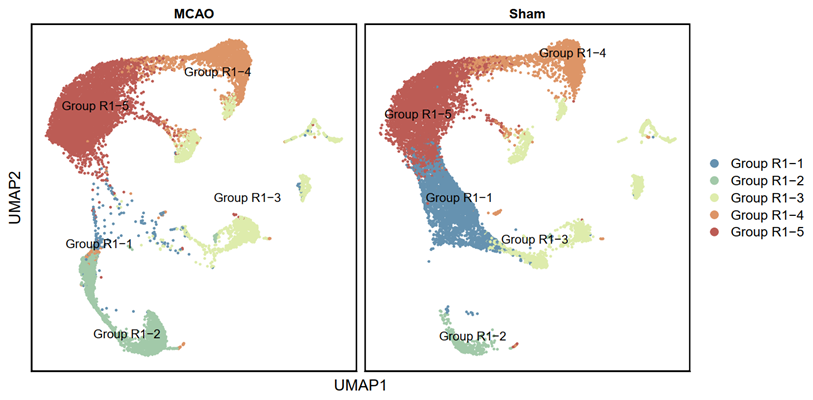
p2 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "Biaoqian", split.by = "Group", pt.size=0.5, label = T, repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 3A-2.pdf", plot = p2, device = 'pdf', width = 26, height = 14, units = 'cm')
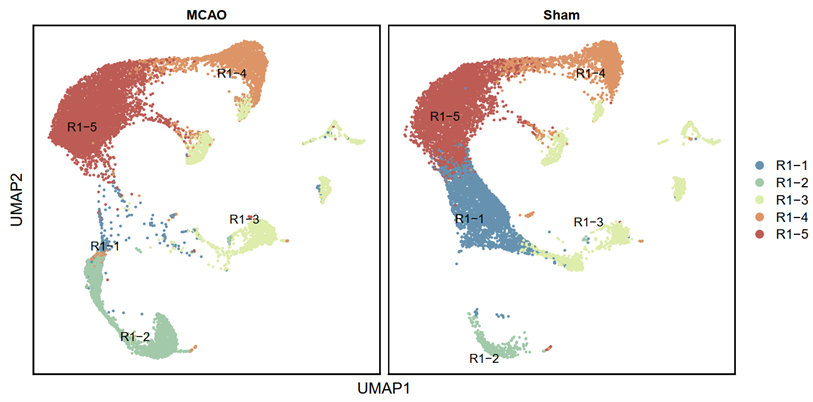
2.3.3 Export cell proportions (R)
Table1 <- table(testAB.integrated$Group, testAB.integrated$ranse)
write.table(Table1, file = "Cell counts-group.txt", sep ="\t")
2.3.4 Plot cells elevated compared to MCAO group (R)
tb <- data.frame(table(testAB.integrated$ranse,testAB.integrated$Sample, testAB.integrated$Group))
tb=tb[,c(1,3,4)]
2.3.5 Calculate Percentages (R)
tb$Total <- apply(tb,1,function(x)sum(tb[tb$Var3 == x[2],3]))
tb<- tb %>% mutate(Percentage = round(Freq/Total,3) * 100)
tb=tb[,c(1,2,5)]
tb$Var1=as.factor(tb$Var1)
tb$Var3=as.factor(tb$Var3)
head(tb)
2.3.6 Perform t-Tests (R)
df= do.call(rbind,
lapply(split(tb,tb$Var1), function(x){
# x= split(tb,tb$Var1)[[1]]
tmp = t.test(x$Percentage ~ x$Var3)
return(c(tmp$p.value, tmp$estimate[1]-tmp$estimate[2]))
}))
2.3.7 Add Threshold Labels (R)
colnames(df) = c("pval","Difference")
df = as.data.frame(df)
df$threshold = factor(ifelse(df$Difference > 0 ,'Down','Up'))
2.3.8 Visualization (R)
ggplot(df,aes(x=Difference,y=-log10(pval),color=threshold))+
geom_point()+
geom_text_repel(
aes(label = rownames(df)),
size = 4,
segment.color = "black", show.legend = FALSE ) + #add cell name
theme_bw()+# Modify plot background
theme(legend.title = element_blank()) + # Hide legend title
ylab('-log10(pval)')+ # Update Y-axis label
xlab('Difference')+ # Update X-axis label
geom_vline(xintercept=c(0),lty=3,col="black",lwd=0.5)
ggsave("Figure 3C.pdf",width = 5,height = 3.8)
save(testAB.integrated,file = 'GSE232429 Neuron.Rdata')
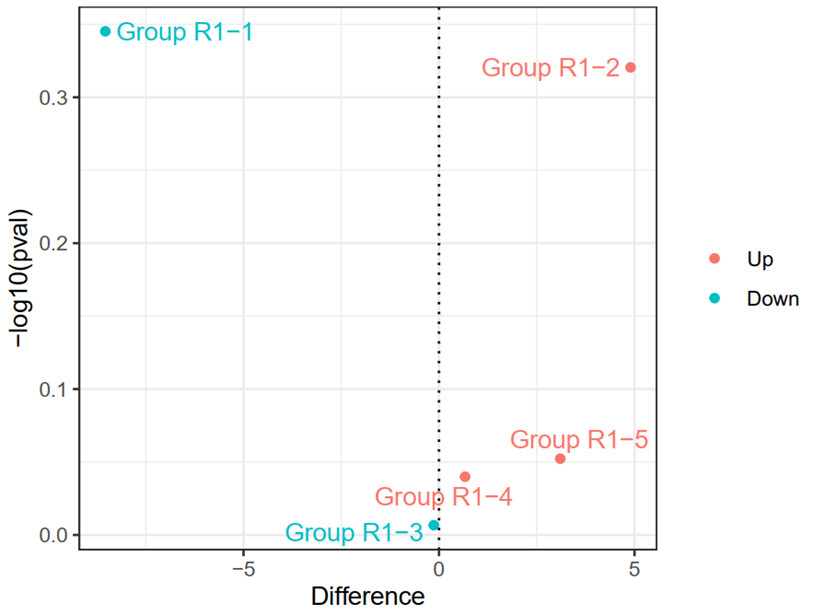
2.3.9 Load required packages (R)
library(Seurat)
library(multtest)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(patchwork)
library(tidyverse)
library(future)
library(RColorBrewer)
library(SummarizedExperiment)
library(scater)
library(cowplot)
library(harmony)
library(monocle3)
library(uwot)
library(ComplexHeatmap)
library(ggrepel)
library(DEsingle)
2.3.10 DEG analysis for GSE232429 (R)
library(SingleCellExperiment)
library(DEsingle)
testAB.integrated[["RNA"]] <- as(object = testAB.integrated[["RNA"]], Class = "Assay")
2.3.11 Set active.ident to ranse (R)
Idents(testAB.integrated) <- "ranse"
DefaultAssay(testAB.integrated) <- "RNA"
2.3.12 Perform pairwise comparisons (R)
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-1", "Group R1-2"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-1 vs Group R1-2.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-1", "Group R1-3"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-1 vs Group R1-3.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-1", "Group R1-4"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-1 vs Group R1-4.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-1", "Group R1-5"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-1 vs Group R1-5.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-2", "Group R1-3"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-2 vs Group R1-3.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-2", "Group R1-4"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-2 vs Group R1-4.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-2", "Group R1-5"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-2 vs Group R1-5.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-3", "Group R1-4"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-3 vs Group R1-4.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-3", "Group R1-5"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-3 vs Group R1-5.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R1-4", "Group R1-5"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$ranse)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R1-4 vs Group R1-5.csv")
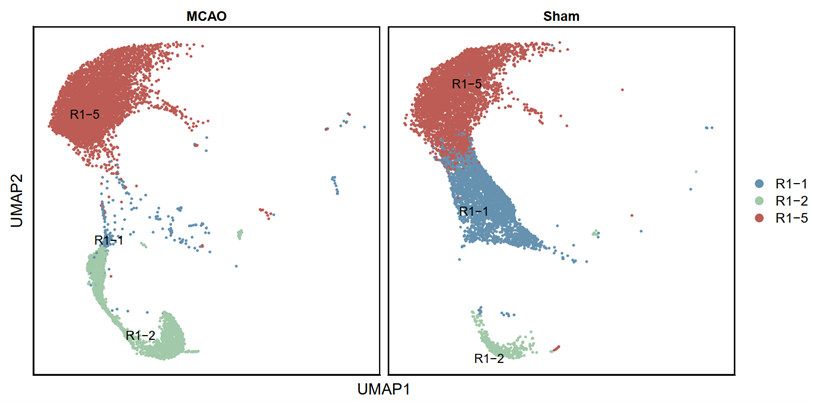
2.3.13 Based on all the results, groups 1, 2, and 5 were included in the subsequent analysis (R)
load("C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429/GSE232429 Neuron.Rdata")
Idents(testAB.integrated) <- "Biaoqian"
testAB.integrated <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("R1-1","R1-2","R1-5"),invert = FALSE)
cell_type_cols <- c("#6693b1","#a3caa9","#bd5c56")
p2 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "ranse", split.by = "Group", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 3E-1.pdf", plot = p2, device = 'pdf', width = 26, height = 14, units = 'cm')
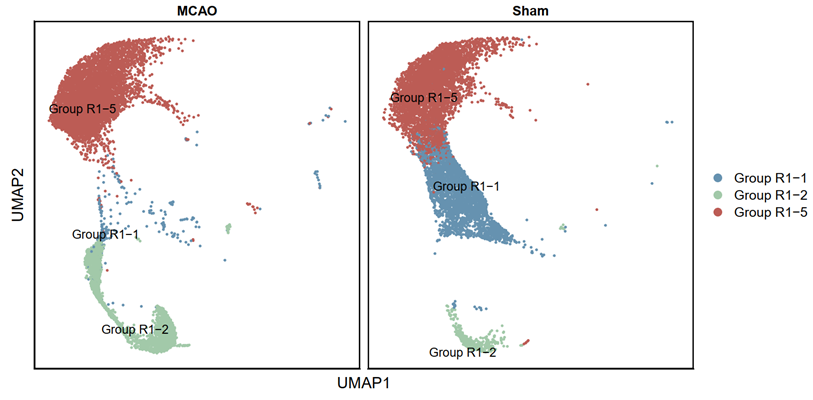
2.3.14 Visualization (R)
p3 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "Biaoqian", split.by = "Group", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 3E-2.pdf", plot = p3, device = 'pdf', width = 26, height = 14, units = 'cm')
save(testAB.integrated,file = 'GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata')
2.3.15 Save .h5ad (R)
################# Rdata to h5ad #########################
library(SeuratDisk)
convert_Rdata_to_H5AD <- function(rdata_path) {
file_dir <- dirname(rdata_path)
file_name <- tools::file_path_sans_ext(basename(rdata_path))
load(rdata_path)
object_names <- ls()
# 检查是否为 Seurat 对象
for (obj_name in object_names) {
obj <- get(obj_name)
if (inherits(obj, "Seurat")) {
# 保存为 H5Seurat 格式
h5seurat_path <- file.path(file_dir, paste0(file_name, "_", obj_name, ".h5Seurat"))
SaveH5Seurat(obj, filename = h5seurat_path)
# 转换为 H5AD 格式
h5ad_path <- file.path(file_dir, paste0(file_name, "_", obj_name, ".h5ad"))
Convert(h5seurat_path, dest = "h5ad")
cat("Conversion complete for object", obj_name, ". H5AD file saved at:", h5ad_path, "/n")
}
}
}
################# Export H5AD #########################
testAB.integrated=get(load(file = 'GSE232429 Neuron.Rdata'))
Idents(testAB.integrated) <- "Biaoqian"
testAB.integrated <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("R1-1","R1-2","R1-5"),invert = FALSE)# Save the file as h5ad for further analysis in Python
# Because the group was removed, UMAP and PCA were redrawn
testAB.integrated = SCTransform(testAB.integrated,assay = 'RNA')
testAB.integrated = RunPCA(testAB.integrated)
ElbowPlot(testAB.integrated)
testAB.integrated = RunUMAP(testAB.integrated,dims = 1:10)#调umap图的参数
testAB.integrated[["integrated"]] <- NULL #删掉integrated
save(testAB.integrated,file = 'For_H5AD_GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata')
#Export H5AD Files
# args <- commandArgs(trailingOnly = TRUE)
args <- "For_H5AD_GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata"#工作路径下的Rdata文件
if (length(args) == 0) {
stop("No .Rdata file path provided. Usage: Rscript script_name.R <path_to_Rdata>")
}
rdata_path <- args[1]
convert_Rdata_to_H5AD(rdata_path)
Save variable table as Round1.Rdata to continue. OR: Do not close R to ensure the subsequent programs can run.
Get the file For_H5AD_GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4_testAB.integrated.h5ad and rename it to 2024.10.28_Group15-21.h5ad
Round 2
3 𝘿𝙞𝙨𝙩𝙞𝙣𝙜𝙪𝙞𝙨𝙝 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙨𝙩𝙖𝙜𝙚𝙨 𝙤𝙛 𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙧𝙤𝙥𝙩𝙤𝙨𝙞𝙨 𝙞𝙣 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡𝙨. 𝘿𝙪𝙚 𝙩𝙤 𝙨𝙝𝙖𝙧𝙚𝙙 𝙍𝙉𝘼 𝙥𝙖𝙩𝙝𝙬𝙖𝙮𝙨, 𝙢𝙖𝙣𝙮 𝙘𝙚𝙡𝙡𝙨 𝙪𝙣𝙙𝙚𝙧𝙜𝙤𝙞𝙣𝙜 𝙖𝙥𝙤𝙥𝙩𝙤𝙨𝙞𝙨 𝙖𝙧𝙚 𝙢𝙞𝙭𝙚𝙙 𝙞𝙣.
Start
3.1 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟏: 𝐀𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐚𝐭𝐞 𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐱𝐢𝐦𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐦𝐞𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐝. (Python)
Import 2024.10.28_Group15-21.h5ad into [LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis_remove_R1_3_4\data\2024.10.28_Group15-21.h5ad.
import numpy as np
import os
import LittleSnowFox as kl
#import matlab.engine
#eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab()
print(kl.__version__)
# Initialization function to switch Kailin to the working directory.
# If it has been initialized before, running def kl_initialize(0) again
# will reject reinitialization to avoid recursion.
# Running def kl_initialize(1) will forcibly reinitialize.
kl.kl_initialize(0)
# Retrieve the root directory where Kailin works
parent_directory_origin = kl.kl_settings.parent_directory_origin
print(parent_directory_origin)
current_folder = kl.workcatalogue.choosemode_kl(parent_directory_origin,'Lineage',1)
print(current_folder)
# Select which sample to use
choosen_sample = "Nerveferroptosis_remove_R1_3_4"
# Select the .h5ad file
h5ad_filename = "2024.10.28_Group15-21.h5ad"
# Run the built-in example and obtain the sparse matrix
# Here, a non-example function needs to be included
current_folder_input = current_folder
orig_adata, loading_directory, distance_matrix = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix(
choosen_sample,
h5ad_filename,
"draw",
current_folder_input,
1,
13000,
0.1,
0.001,
True
)
# orig_adata, loading_directory, distance_matrix_sparse = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix_sample(
# choosen_sample,
# h5ad_filename,
# "draw",
# current_folder_input
# )
# Run the built-in example and obtain the non-sparse matrix
# Here, a non-example function needs to be included
# current_folder_input = current_folder
# loading_directory, distance_matrix = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix(
# choosen_sample,
# h5ad_filename,
# "draw",
# current_folder_input
# )
print(loading_directory)
print(choosen_sample)
#需要区分dense和sparase
save_list = ["orig_adata.obsm['X_umap']"]
#将要计算的文件保存到/result
merged_csv,result_directory = kl.workcatalogue.kl_save(loading_directory,choosen_sample,distance_matrix,save_list,orig_adata)
3.2 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟐: 𝐔𝐬𝐞 𝐮𝐧𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐧𝐢𝐧𝐠. (Matlab)
Afterward, execute the following file:
[LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis_remove_R1_3_4\main_v3_matlab_run_me.m
%% Load data and Split to compute
MM0 = load('./result/distance_matrix.mat');
MM0 = MM0.distance_matrix;
%% 读取要排序的对象
count_=readtable('./result/merged_data.csv');
%% 得到边界划分点
[p,splitlist] = binary_corr_sorting(MM0,20,500,5,5);%350:72 真实:68
%% 对划分点去重
[uniqueList, ~, ~] = unique(splitlist, 'stable');
%% 对相似度矩阵排序
MM=MM0(p,p);
split=[];
%% 重排count_result
count_result=count_(p,:);
split_simple=uniqueList;
%% 第一个起始位点置为1
split_simple(1)=1;
split_simple=[split_simple,length(MM0)];
%% 计算均值矩阵
[simple_matrix]=sample_computing(count_result,split_simple,MM,"mean");
%% 合并成小矩阵
ClusterReslut=cluster_map(split_simple,simple_matrix,0,0.0002,0);
count_result.Result = ClusterReslut;
%重排小矩阵
[cluster_map_matrix] = genetic_encoder( ...
simple_matrix, ...
60, ...% nPop = 50; % 种群规模大小为30
1, ...% nPc = 1; % 子代规模的比例0.8
200, ...% maxIt = 200; % 最大迭代次数
5 ...% cycletimes = 200; % 循环计算次数
);
%重拍小矩阵方案2
% 创建行和列标签(示例)
%row_labels = cluster_map_label;
%column_labels = cluster_map_label;
% 使用 heatmap 函数并传递相应参数
h = heatmap(cluster_map_matrix);
%h.YDisplayLabels = row_labels; % 设置行标签
%h.XDisplayLabels = column_labels; % 设置列标签
h.ColorLimits = [0, 0.00007]
%----------------------------
figure(1)
h = heatmap(cluster_map_matrix);
h.ColorLimits = [0, 0.00007]
%writetable(count_result,"result/pseudotime_map.csv");
%% 临近法激活
corr_matrix = relevance_generate(0.000072,3,cluster_map_matrix);
heatmap(corr_matrix);
%% 编码
encode_result = encoder_corr_matrix(0.0000731,0.0000729,50,3,cluster_map_matrix);
figure(2)
hj = heatmap(encode_result);
%% 解码
figure(3)
[weighting_decode,decode_result] = decoder_corr_matrix(encode_result);
weighting_result = decode_result;
hk = heatmap(weighting_result);
hk.ColorLimits = [30, 35]
writetable(count_result,"result/pseudotime_map_R2.csv");
3.3 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟑: 𝐏𝐞𝐫𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦 𝐨𝐦𝐢𝐜𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐬. (R)
Open variable table as Round1.Rdata to continue. OR: You didn’t closed R.
3.3.1 Perform pseudo-time inference on groups 1, 2, and 5 (R)
load("C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429/GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata")
testAB.integrated[["RNA4"]] <- as(object = testAB.integrated[["RNA"]], Class = "Assay")
#re-do umap
UMAPPlot(testAB.integrated,group.by='ranse',label=T)
testAB.integrated = SCTransform(testAB.integrated,assay = 'RNA')
testAB.integrated = RunPCA(testAB.integrated)
ElbowPlot(testAB.integrated)
testAB.integrated = RunUMAP(testAB.integrated,dims = 1:10)
UMAPPlot(testAB.integrated,group.by='ranse',label=T)
3.3.2 Extract the matrix to make pseudo time (R)
DefaultAssay(testAB.integrated) <- "RNA4"
data <- as(as.matrix(testAB.integrated@assays$RNA4@counts), 'sparseMatrix')
pd <- new('AnnotatedDataFrame',
data = testAB.integrated@meta.data)
fData <- data.frame(gene_short_name = row.names(data),
row.names = row.names(data))
fd <- new('AnnotatedDataFrame', data = fData)
pd <- as(pd, "data.frame")
fd <- as(fd, "data.frame")
#Start make pseudo time
cds <- new_cell_data_set(data,
cell_metadata = pd
,gene_metadata = fd)
cds <- preprocess_cds(cds, num_dim = 10)
cds <- reduce_dimension(cds, reduction_method = "UMAP")
cds <- cluster_cells(cds, resolution = 0.000001)
plot_cells(cds, color_cells_by = "ranse",show_trajectory_graph = F,group_label_size=12)
#Replace the original umap data
cds@int_colData@listData[["reducedDims"]]@listData[["UMAP"]][,1] = testAB.integrated@reductions$umap@cell.embeddings[,1]
cds@int_colData@listData[["reducedDims"]]@listData[["UMAP"]][,2] = testAB.integrated@reductions$umap@cell.embeddings[,2]
#Continue to the next step
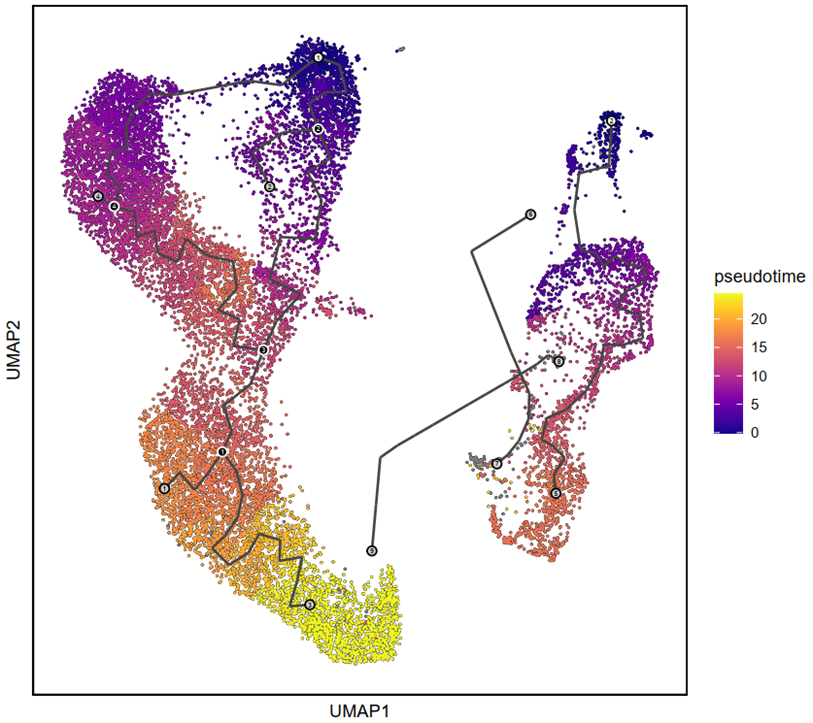
cds <- learn_graph(cds)
cds <- order_cells(cds)
p3 <- plot_cells(cds,
color_cells_by = "pseudotime",
label_cell_groups = T,
label_leaves = TRUE,
label_branch_points = TRUE,
graph_label_size = 1.5) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 4A.pdf", plot = p3, device = 'pdf', width = 18, height = 16, units = 'cm')
save(testAB.integrated,file = 'GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata')
3.3.3 Regroup 1, 2, and 5 (R)
Place pseudotime_map_R2.csv in the R working directory.
File is usuallly located at C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429/pseudotime_map_R2.csv
testAB.integrated=get(load(file = 'GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata'))
#Import the new grouping results
# Read CSV file
result_data <- read.csv("pseudotime_map_R2.csv", stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
# Ensure the file contains columns 'Var1' and 'Result'; check file content
head(result_data)
# Check if all 'Var1' values exist in Seurat object's cell names
common_cells <- intersect(result_data$Var1, rownames(testAB.integrated@meta.data))
if (length(common_cells) < nrow(result_data)) {
warning("Some cells in 'pseudotime_map.csv' are not found in testAB.integrated metadata!")
}
3.3.4 Map ‘Result’ values to Seurat object’s metadata based on ‘Var1’ (R)
# First, create a new column 'Result' and set it to NA
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Result <- NA
# Use match() to merge corresponding values
matching_indices <- match(rownames(testAB.integrated@meta.data), result_data$Var1)
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Result <- result_data$Result[matching_indices]
## Group based on 'Result'
# get metadata
metadata <- testAB.integrated@meta.data
# Create a new column shijian based on the value of the Result column
metadata$shijian <- with(metadata,
ifelse(Result >= 1 & Result <= 14, "Group R2-1",
ifelse(Result >= 15 & Result <= 18, "Group R2-2",
ifelse(Result >= 19 & Result <= 21, "Group R2-3",
ifelse(Result == 22, "Group R2-4",
ifelse(Result == 23, "Group R2-5",
ifelse(Result == 24, "Group R2-6",
ifelse(Result == 25, "Group R2-7",
ifelse(Result >= 26 & Result <= 44, "Group R2-8",
ifelse(Result == 45, "Group R2-9", NA)))))))))
)
3.3.5 Build the Biaoqian column, remove the “Group” in time (R)
metadata$Biaoqian <- gsub("^Group ", "", metadata$shijian)
3.3.6 Assign updated metadata back to the Seurat object (R)
testAB.integrated@meta.data <- metadata
3.3.7 Check results (R)
head(testAB.integrated@meta.data)
#Save
save(testAB.integrated,file = 'GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata')
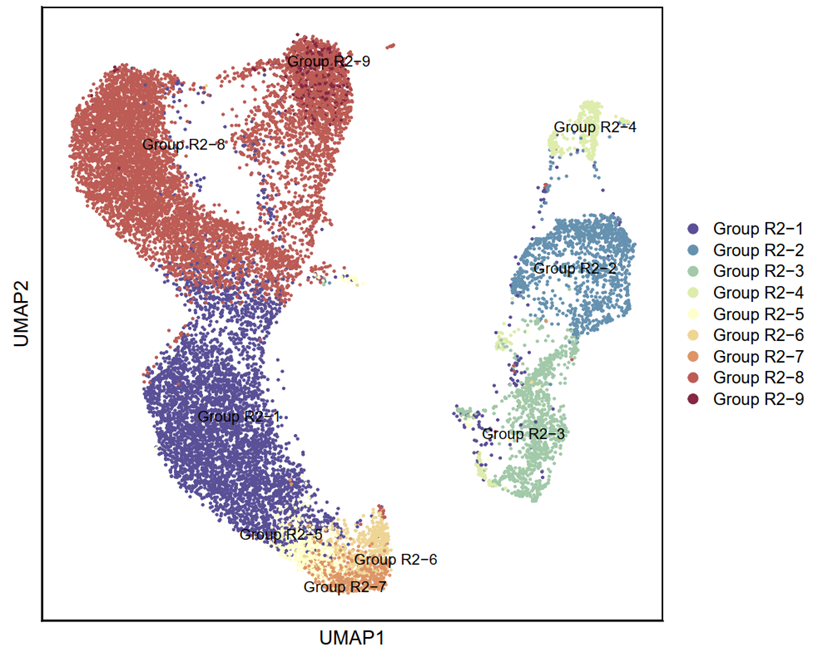
3.3.8 Plotting (R)
#Figure 4C
cell_type_cols <- c("#5a5098","#6693b1","#a3caa9","#deedad","#ffffcc","#efd695","#dd9667","#bd5c56","#842844")
p4 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "shijian", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 4C-1.pdf", plot = p4, device = 'pdf', width = 21, height = 18, units = 'cm')
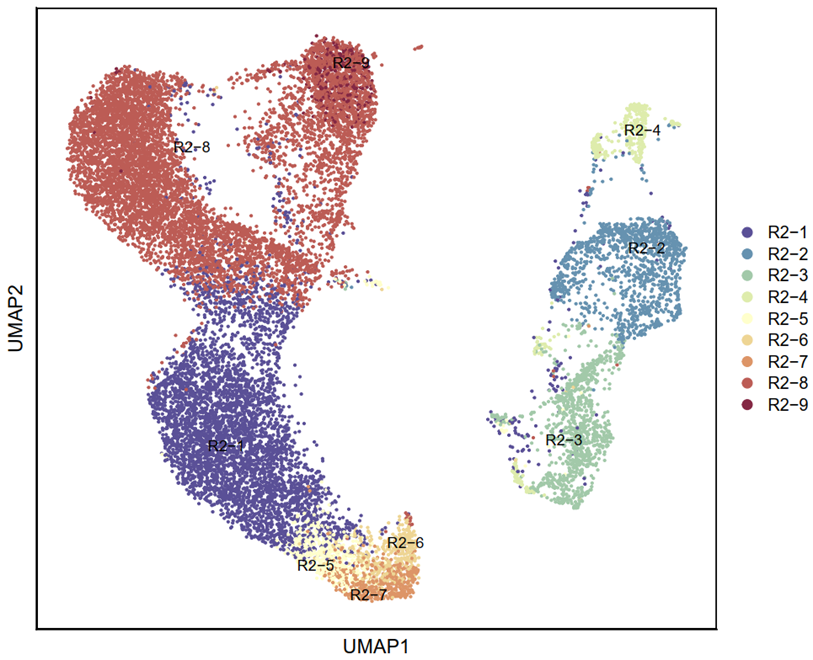
3.3.9 Visualization (R)
p5 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "Biaoqian", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 4C-2.pdf", plot = p5, device = 'pdf', width = 21, height = 18, units = 'cm')
3.3.10 Export cell proportions (R)
# Table1 <- table(testAB.integrated$newresults)
# write.table(Table1, file = "The number of cells per cluster.txt", sep ="\t")
cell_type_cols <- c("#5a5098","#6693b1","#a3caa9","#deedad","#ffffcc","#efd695","#dd9667","#bd5c56","#842844")
p5 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "shijian", split.by = "Group", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 4E-1.pdf", plot = p5, device = 'pdf', width = 26, height = 14, units = 'cm')
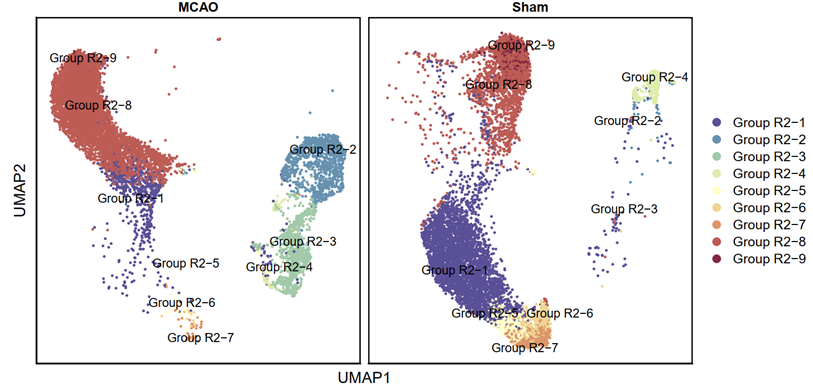
3.3.11 Visualization (R)
p6 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "Biaoqian", split.by = "Group", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 4E-2.pdf", plot = p6, device = 'pdf', width = 26, height = 14, units = 'cm')
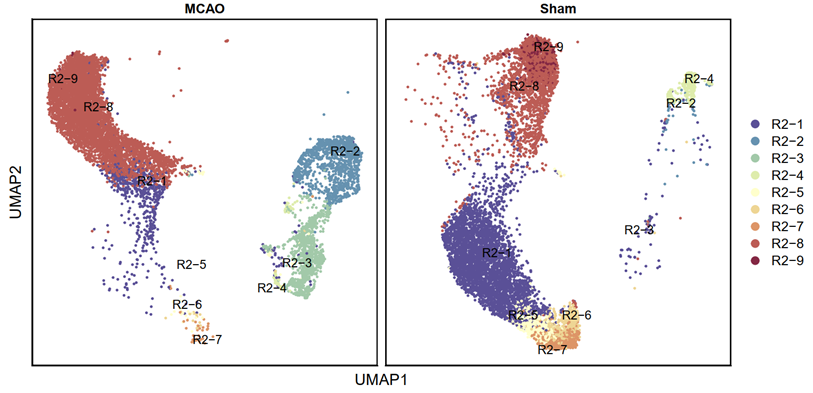
3.3.12 Group Difference (R)
# Table1 <- table(testAB.integrated$Group, testAB.integrated$shijian2)
# write.table(Table1, file = "The cell proportion of the new grouping result-group.txt", sep ="\t")
# Plot cells elevated compared to MCAO group
tb <- data.frame(table(testAB.integrated$shijian,testAB.integrated$Sample, testAB.integrated$Group))
tb=tb[,c(1,3,4)]
tb$Total <- apply(tb,1,function(x)sum(tb[tb$Var3 == x[2],3]))
tb<- tb %>% mutate(Percentage = round(Freq/Total,3) * 100)
tb=tb[,c(1,2,5)]
tb$Var1=as.factor(tb$Var1)
tb$Var3=as.factor(tb$Var3)
head(tb)
df= do.call(rbind,
lapply(split(tb,tb$Var1), function(x){
# x= split(tb,tb$Var1)[[1]]
tmp = t.test(x$Percentage ~ x$Var3)
return(c(tmp$p.value, tmp$estimate[1]-tmp$estimate[2]))
}))
colnames(df) = c("pval","Difference")
df = as.data.frame(df)
df$threshold = factor(ifelse(df$Difference > 0 ,'Down','Up'))
ggplot(df,aes(x=Difference,y=-log10(pval),color=threshold))+
geom_point()+
geom_text_repel(
aes(label = rownames(df)),
size = 4,
segment.color = "black", show.legend = FALSE ) +
theme_bw()+# Modify plot background
theme(legend.title = element_blank()) + # Hide legend title
ylab('-log10(pval)')+ # Update Y-axis label
xlab('Difference')+ # Update X-axis label
geom_vline(xintercept=c(0),lty=3,col="black",lwd=0.5)
ggsave("Figure 4G.pdf",width = 5,height = 3.8)
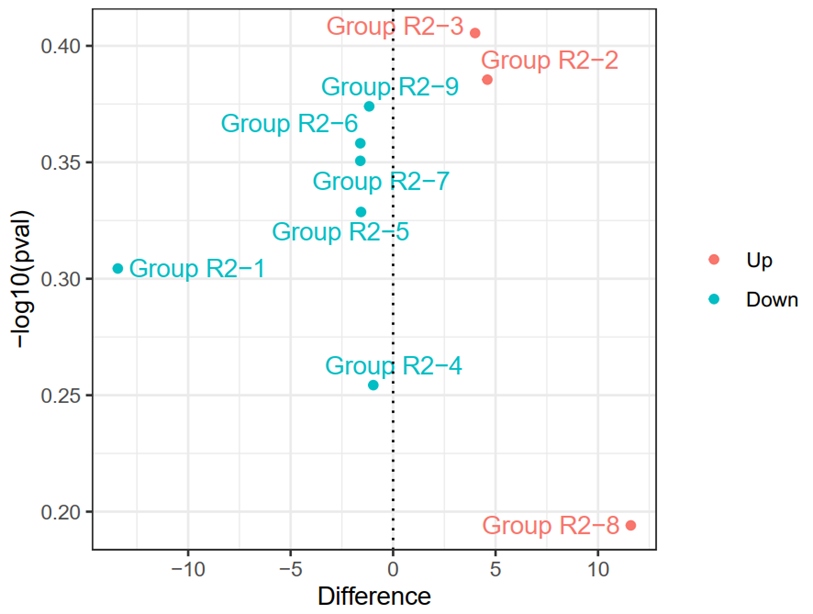
3.3.13 Do DEG analysis for regrouping results (R)
testAB.integrated[["RNA"]] <- as(object = testAB.integrated[["RNA"]], Class = "Assay")
#set active.ident to shijian
Idents(testAB.integrated) <- "shijian"
DefaultAssay(testAB.integrated) <- "RNA"
#Do DEG analysis
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R2-1", "Group R2-5"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$shijian)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R2-1 vs Group R2-5.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R2-1", "Group R2-6"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$shijian)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R2-1 vs Group R2-6.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R2-1", "Group R2-7"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$shijian)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R2-1 vs Group R2-7.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R2-3", "Group R2-5"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$shijian)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R2-3 vs Group R2-5.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R2-3", "Group R2-6"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$shijian)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R2-3 vs Group R2-6.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R2-3", "Group R2-7"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$shijian)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R2-3 vs Group R2-7.csv")
s0 <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Group R2-2", "Group R2-4"),invert = FALSE)
s0 <- as.SingleCellExperiment(s0)
group0 <- factor(s0$shijian)
results0 <- DEsingle(counts = s0, group = group0, parallel = TRUE)
write.csv(results0, file="Group R2-2 vs Group R2-4.csv")
3.3.14 After determining the head and tail, we will find the differential genes of the head and tail cell groups (R)
testAB.integrated=get(load(file = 'GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata'))
DefaultAssay(testAB.integrated) <- "RNA"
testAB.integrated <- JoinLayers(testAB.integrated)
Idents(testAB.integrated) <- "shijian"
chayi1 <- FindMarkers(testAB.integrated, ident.1 = "Group R2-3", ident.2 = "Group R2-9",
assay = "RNA", slot="counts",
only.pos = F, min.pct = 0, logfc.threshold = 0)
write.csv(chayi1, file="Differential genes between Group R2-3 and Group R2-9.csv")
3.3.15 Save .h5ad (R)
testAB.integrated=get(load(file = 'GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata'))
DefaultAssay(testAB.integrated) <- "RNA" ####这个是我刚刚插入的
testAB.integrated[["RNA"]] <- as(object = testAB.integrated[["RNA"]], Class = "Assay")#转成版本4的矩阵
testAB.integrated[["RNA4"]] <- NULL #去掉RNA4
testAB.integrated[["SCT"]] <- NULL #去掉SCT
testAB.integrated[["integrated"]] <- NULL #去掉SCT
Idents(testAB.integrated) <- "Biaoqian"
testAB.integrated <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("R2-2","R2-3"),invert = FALSE)
Idents(testAB.integrated) <- "Group"
testAB.integrated <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("MCAO"),invert = FALSE)
###First generate h5ad for further analysis###
# Make sure you select a matrix that contains all genes
sceasy::convertFormat(
testAB.integrated,
from = "seurat",
to = "anndata",
outFile = "Group R2-2 R2-3.h5ad"
)
Save variable table as Round2.Rdata to continue. OR: Do not close R to ensure the subsequent programs can run.
Round 3
4 𝙑𝙚𝙧𝙞𝙛𝙮 𝙩𝙝𝙚 𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙧𝙤𝙥𝙩𝙤𝙨𝙞𝙨 𝙧𝙖𝙩𝙞𝙤, 𝙙𝙞𝙨𝙩𝙞𝙣𝙜𝙪𝙞𝙨𝙝 𝙗𝙚𝙩𝙬𝙚𝙚𝙣 𝙛𝙚𝙧𝙧𝙤𝙥𝙩𝙤𝙨𝙞𝙨 𝙖𝙣𝙙 𝙖𝙥𝙤𝙥𝙩𝙤𝙨𝙞𝙨.
Start
4.1 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟏: 𝐀𝐜𝐭𝐢𝐯𝐚𝐭𝐞 𝐮𝐬𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐩𝐫𝐨𝐱𝐢𝐦𝐢𝐭𝐲 𝐦𝐞𝐭𝐡𝐨𝐝. (Python)
Import Group R2-2 R2-3.h5ad into [LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis_15_21\data\Group R2-2 R2-3.h5ad.
import numpy as np
import os
import LittleSnowFox as kl
#import matlab.engine
#eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab()
print(kl.__version__)
#初始化函数,将LittleSnowFox转至工作目录。如果此前初始化过,那么在再次运行def kl_initialize(0)时,
#则拒绝初始化,避免套娃。运行def kl_initialize(1)时,强制重新初始化。
kl.kl_initialize(0)
#获取kailin工作的根目录
parent_directory_origin = kl.kl_settings.parent_directory_origin
print(parent_directory_origin)
#改进:
#添加一个cluster模式
#选择进行Lineage Tracing还是Cluster,并给出可用的列表
current_folder = kl.workcatalogue.choosemode_kl(parent_directory_origin,'Lineage',1)
print(current_folder)
#选择要使用哪个样本
choosen_sample = "Nerveferroptosis_15_21"
#选择.h5ad文件
h5ad_filename = "Group R2-2 R2-3.h5ad"
#运行自带的示例,并获取稀疏矩阵
#这里需要做非示例的函数进去
current_folder_input = current_folder
orig_adata,loading_directory,distance_matrix = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix(choosen_sample,h5ad_filename,"draw",current_folder_input,1,13000,0.1,0.001,True)
print(loading_directory)
print(choosen_sample)
#需要区分dense和sparase
save_list = ["orig_adata.obsm['X_umap']", "orig_adata.obs['shijian']"]
#将要计算的文件保存到/result
merged_csv,result_directory = kl.workcatalogue.kl_save(loading_directory,choosen_sample,distance_matrix,save_list,orig_adata)
4.2 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟐: 𝐔𝐬𝐞 𝐮𝐧𝐬𝐮𝐩𝐞𝐫𝐯𝐢𝐬𝐞𝐝 𝐥𝐞𝐚𝐫𝐧𝐢𝐧𝐠. (Matlab)
Afterward, execute the following file:
[LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis_15_21\main_v3_matlab_run_me_15_21.m
clc;clear
%% Load data and Split to compute
%% Load data and Split to compute
MM0 = load('./result/distance_matrix.mat');
MM0 = MM0.distance_matrix;
%% 读取要排序的对象
count_=readtable('./result/merged_data.csv');
%% 得到边界划分点
%[p,splitlist] = binary_corr_sorting(MM0,20,125,5,5);
[p,splitlist] = binary_corr_sorting(MM0,20,100,5,5);
%% 对划分点去重
[uniqueList, ~, ~] = unique(splitlist, 'stable');
%% 对相似度矩阵排序
MM=MM0(p,p);
split=[];
%% 重排count_result
count_result=count_(p,:);
split_simple=uniqueList;
%% 第一个起始位点置为1
split_simple(1)=1;
split_simple=[split_simple,length(MM0)];
%% 计算均值矩阵
[simple_matrix]=sample_computing(count_result,split_simple,MM,"mean");
%% 合并成小矩阵
ClusterReslut=cluster_map(split_simple,simple_matrix,0,0.0002,0);
count_result.Result = ClusterReslut;
%重排小矩阵
[cluster_map_matrix] = genetic_encoder( ...
simple_matrix, ...
60, ...% nPop = 50; % 种群规模大小为30
1, ...% nPc = 1; % 子代规模的比例0.8
200, ...% maxIt = 200; % 最大迭代次数
5 ...% cycletimes = 200; % 循环计算次数
);
%重拍小矩阵方案2
% 创建行和列标签(示例)
%row_labels = cluster_map_label;
%column_labels = cluster_map_label;
% 使用 heatmap 函数并传递相应参数
h = heatmap(cluster_map_matrix);
%h.YDisplayLabels = row_labels; % 设置行标签
%h.XDisplayLabels = column_labels; % 设置列标签
h.ColorLimits = [0.00005,0.0003]%
%writetable(count_result, './result/result_group.csv');
%% 临近法激活
corr_matrix = relevance_generate(0.00065,4,cluster_map_matrix);
hi = heatmap(corr_matrix);
%% 编码
encode_result = encoder_corr_matrix(0.0007,0.0006,1,4,cluster_map_matrix);
figure(2)
hj = heatmap(encode_result);
%% 解码
figure(3)
[weighting_decode,decode_result] = decoder_corr_matrix(encode_result);
weighting_result = weighting_decode + decode_result;
hk = heatmap(decode_result);
hk.ColorLimits = [26,27]
writetable(count_result,"result/pseudotime_map_R3.csv");
4.3 𝐒𝐭𝐞𝐩 𝟑: 𝐏𝐞𝐫𝐟𝐨𝐫𝐦 𝐨𝐦𝐢𝐜𝐬 𝐚𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐢𝐬. (R)
Distinguish between ferroptosis and apoptosis
Read variable table as Round2.Rdata to continue. OR: You didn’t closed R.
4.3.1 Cells from Group R2-2 and Group R2-3 of the MCAO group were taken for further analysis (R)
Place pseudotime_map_R3.csv in the R working directory. File is usuallly located at C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE232429/
####Then I got 15-21-result.csv, so I imported it
# Read CSV file
result_data <- read.csv("pseudotime_map_R3.csv", stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
# Make sure the columns in the file are named "Var1" and "Result", check the file contents
head(result_data)
# Check if all Var1 have corresponding cell names in the Seurat object
common_cells <- intersect(result_data$Var3, rownames(testAB.integrated@meta.data))
if (length(common_cells) < nrow(result_data)) {
warning("Some cells in '15-21-result.csv' are not found in testAB.integrated metadata!")
}
# Import Result into the metadata of the Seurat object according to Var1
# First create a new column "Result" and assign it to NA
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Result <- NA
# Use match() to merge the corresponding relationships
matching_indices <- match(rownames(testAB.integrated@meta.data), result_data$Var3)
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Result <- result_data$Result[matching_indices]
##Group by Result
# Get metadata
metadata <- testAB.integrated@meta.data
# Create a new column fenqun1 based on the value of the Result column
metadata$fenqun1 <- with(metadata,
ifelse(Result >= 1 & Result <= 5, "Group R3-1",
ifelse(Result >= 6 & Result <= 11, "Group R3-2",
ifelse(Result >= 12 & Result <= 19, "Group R3-3",
ifelse(Result >= 20 & Result <= 27, "Group R3-4",
ifelse(Result >= 28 & Result <= 34, "Group R3-5", NA))))))
# Construct the Biaoqian column and remove the "Group" in fenqun1
metadata$Biaoqian <- gsub("^Group ", "", metadata$fenqun1)
# Assign updated metadata back to the Seurat object
testAB.integrated@meta.data <- metadata
# Check results
head(testAB.integrated@meta.data)
#Save
save(testAB.integrated,file = 'Cells from Group R2-2 and Group R2-3.Rdata')
4.3.2 Drawing (R)
cell_type_cols <- c("#6693b1","#a3caa9","#efd695","#dd9667","#bd5c56")
testAB.integrated = RunPCA(testAB.integrated)
ElbowPlot(testAB.integrated)
testAB.integrated = RunUMAP(testAB.integrated,dims = 1:20)
p5 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "fenqun1", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 6A-1.pdf", plot = p5, device = 'pdf', width = 15, height = 12, units = 'cm')
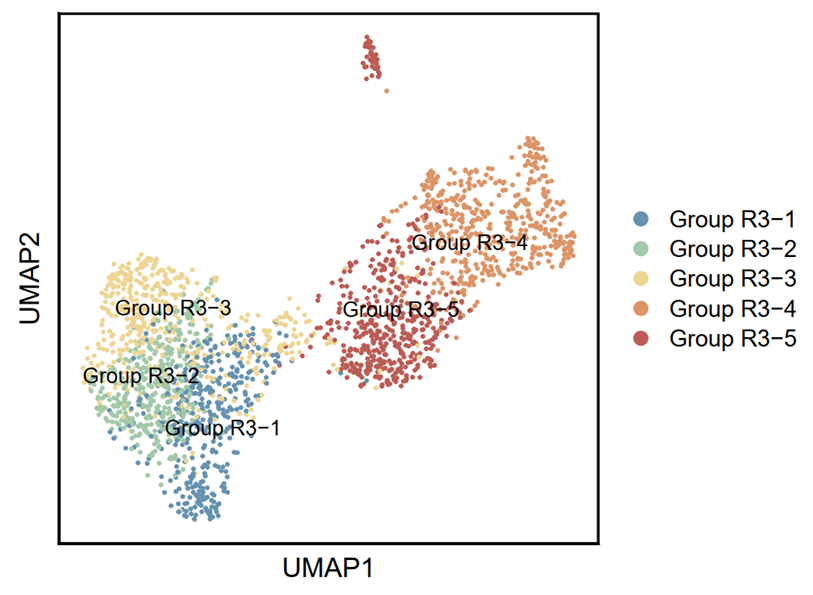
4.3.3 Visualization (R)
p6 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "Biaoqian", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Figure 6A-2.pdf", plot = p6, device = 'pdf', width = 15, height = 12, units = 'cm')
Read variable table as Round2.Rdata to continue. OR: You didn’t closed R.
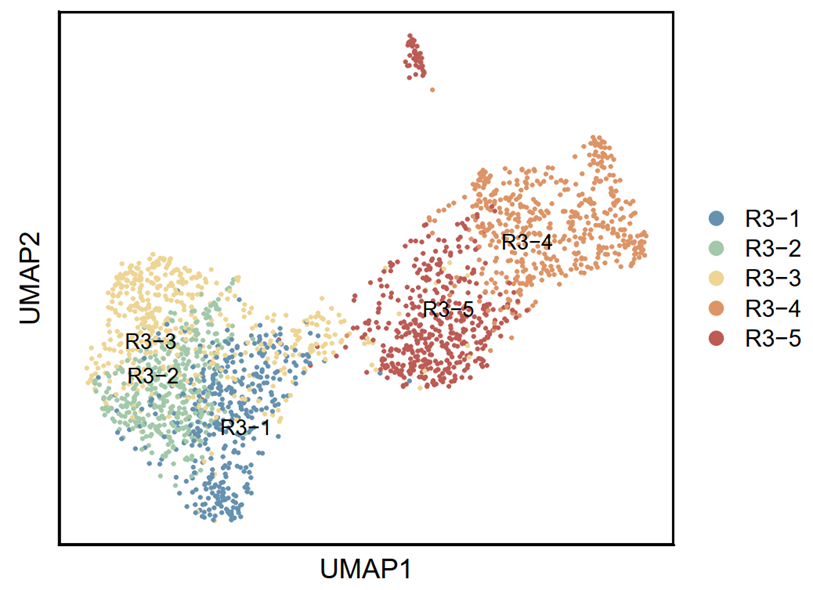
4.3.4 Save .h5ad (R)
#############Take out Group R3-4 and Group R3-5 and merge them with healthy cells #############
R2_cell_data=get(load(file = 'GSE232429 after removing 3 and 4.Rdata'))#Get the data of round 2
R3_cell_data=get(load(file = 'Cells from Group R2-2 and Group R2-3.Rdata'))#get the data of round 3
# Extract the shijian column from the metadata of R2_cell_data
R2_metadata <- R2_cell_data@meta.data
R2_metadata$Extract <- "Other" # Create a new column Extract and initialize it to "Other"
# Set Group R2-8 and Group R2-9 in the shijian to "Health"
R2_metadata$Extract[R2_metadata$shijian %in% c("Group R2-8", "Group R2-9")] <- "Health"
# Extract the fenqun1 column from the metadata of R3_cell_data
R3_metadata <- R3_cell_data@meta.data
# Find the names of the cells in Group R3-4 and Group R3-5 in R3
group_R3_4_cells <- rownames(R3_metadata[R3_metadata$fenqun1 == "Group R3-4", ])
group_R3_5_cells <- rownames(R3_metadata[R3_metadata$fenqun1 == "Group R3-5", ])
# Label the cell names of Group R3-4 and Group R3-5 in R3 in the Extract column in R2
R2_metadata$Extract[rownames(R2_metadata) %in% group_R3_4_cells] <- "Group R3-4"
R2_metadata$Extract[rownames(R2_metadata) %in% group_R3_5_cells] <- "Group R3-5"
# Update the metadata of R2_cell_data
R2_cell_data@meta.data <- R2_metadata
#Check
table(R2_cell_data@meta.data$Extract)
##Get Health, Group R3-4 and Group R3-5
Idents(R2_cell_data) <- "Extract"
Health_4_5 <- subset(R2_cell_data,idents=c("Health","Group R3-5","Group R3-4"),invert = FALSE)
DefaultAssay(Health_4_5) <- "RNA"
Health_4_5[["integrated"]] <- NULL
Health_4_5[["SCT"]] <- NULL
Health_4_5[["RNA"]] <- as(object = Health_4_5[["RNA"]], Class = "Assay")#Convert to version 4 matrix
sceasy::convertFormat(
Health_4_5,
from = "seurat",
to = "anndata",
outFile = "2024_GROUP4_5.h5ad"
)
4.4 Check the coverage of genes. (Python)
import numpy as np
import os
import LittleSnowFox as kl
#import matlab.engine
#eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab()
print(kl.__version__)
#初始化函数,将kailin转至工作目录。如果此前初始化过,那么在再次运行def kl_initialize(0)时,
#则拒绝初始化,避免套娃。运行def kl_initialize(1)时,强制重新初始化。
kl.kl_initialize(0)
#获取kailin工作的根目录
parent_directory_origin = kl.kl_settings.parent_directory_origin
print(parent_directory_origin)
#改进:
#添加一个cluster模式
#选择进行Lineage Tracing还是Cluster,并给出可用的列表
current_folder = kl.workcatalogue.choosemode_kl(parent_directory_origin,'Lineage',1)
print(current_folder)
#选择要使用哪个样本
choosen_sample = "Nerveferroptosis_19_21"
#选择.h5ad文件
h5ad_filename = "2024_GROUP4_5.h5ad"
#运行自带的示例,并获取稀疏矩阵
#这里需要做非示例的函数进去
current_folder_input = current_folder
updated_folder = os.path.join(current_folder, "Nerveferroptosis_19_21/data")
result_folder = os.path.join(current_folder, "Nerveferroptosis_19_21/result")
h5ad_path = os.path.join(updated_folder, "2024_GROUP4_5.h5ad")
print(h5ad_path)
import anndata as ad
adata = ad.read_h5ad(h5ad_path)
adata_Health_RNA = adata[adata.obs['Extract'] == 'Health'].var.index.tolist()
# 获取特定层的形状
length_of_adata_Healt_RNA = len(adata_Health_RNA)
print(adata.X.shape)
print(length_of_adata_Healt_RNA)
adata_Death_RNA = adata[adata.obs['Extract'] != 'Health'].var.index.tolist()
# 获取特定层的形状
length_of_adata_Death_RNA= len(adata_Death_RNA)
print(adata.X.shape)
print(length_of_adata_Death_RNA)
#Group 4-1
import pandas as pd
# 初始化 check_list 和一个空的 DataFrame
check_list = ['Abcc1',
'Acadsb',
'Aco1',
'Acsf2',
'Acsl1',
'Acsl4',
'Adam23',
'Aebp2',
'Agpat3',
'Agps',
'Alox12',
'Alox15',
'Alox15B',
'Alox5',
'Aloxe3',
'Amn',
'Ano6',
'Aqp3',
'Aqp5',
'Aqp8',
'Arhgef26-As1',
'Asmtl-As1',
'Atf3',
'Atg13',
'Atg16L1',
'Atg3',
'Atg4D',
'Atg5',
'Atg7',
'Atm',
'Atp5Mc3',
'Bach1',
'Bap1',
'Becn1',
'Bid',
'Brd7',
'Brpf1',
'Cars1',
'Ccdc6',
'Cd82',
'Cdca3',
'Cdkn2A',
'Cdo1',
'Cfl1',
'Cgas',
'Chac1',
'Chp1',
'Cirbp',
'Circkdm4C',
'Circpsen1',
'Cltrn',
'Cox4I2',
'Cpeb1',
'Cs',
'Ctsb',
'Cyb5R1',
'Cybb',
'Cygb',
'Cyp4F8',
'Dcaf7',
'Ddr2',
'Dld',
'Dnajb6',
'Dpep1',
'Dpp4',
'Duox1',
'Duox2',
'Egfr',
'Egln2',
'Egr1',
'Elavl1',
'Elovl5',
'Emc2',
'Epas1',
'Ept1',
'Fads1',
'Far1',
'Fbxw7',
'Flt3',
'Foxo4',
'G6Pdx',
'Gabarapl1',
'Gabarapl2',
'Gja1',
'Gls2',
'Gpat4',
'Gria3',
'Gsk3B',
'Gstz1',
'H19',
'Hddc3',
'Hilpda',
'Hmgb1',
'Hotair',
'Hras',
'Hsa_Circ_0008367',
'Idh1',
'Ido1',
'Ifna1',
'Ifna10',
'Ifna13',
'Ifna14',
'Ifna16',
'Ifna17',
'Ifna2',
'Ifna21',
'Ifna4',
'Ifna5',
'Ifna6',
'Ifna7',
'Ifna8',
'Ifng',
'Il1B',
'Ints2',
'Ireb2',
'Kdm5A',
'Kdm5C',
'Kdm6B',
'Keap1',
'Klf2',
'Kmt2D',
'Kras',
'Lce2C',
'Lgmn',
'Lifr',
'Lig3',
'Linc00472',
'Linc00618',
'Lncrna Aabr07017145.1',
'Lonp1',
'Lpcat3',
'Lpin1',
'Lyrm1',
'Map1Lc3A',
'Map3K11',
'Map3K14',
'Mapk1',
'Mapk14',
'Mapk3',
'Mapk8',
'Mapk9',
'Mdm2',
'Mdm4',
'Meg3',
'Mettl14',
'Mfn2',
'Mib1',
'Mib2',
'Micu1',
'Miox',
'Mir135B',
'Mir15A',
'Mir-182-5P',
'Mir302A',
'Mir324',
'Mir335',
'Mir375',
'Mir-378A-3P',
'Mir5096',
'Mir539',
'Mir6852',
'Mir761',
'Mllt1',
'Mmd',
'Mt1Dp',
'Mtch1',
'Mtdh',
'Myb',
'Mycn',
'Ncoa4',
'Ndrg1',
'Nox1',
'Nox3',
'Nox4',
'Nox5',
'Nr1D1',
'Nr1D2',
'Nras',
'Osbpl9',
'Panx1',
'Paqr3',
'Pebp1',
'Pex10',
'Pex12',
'Pex2',
'Pex3',
'Pex6',
'Pgd',
'Pgrmc1',
'Phf21A',
'Phkg2',
'Piezo1',
'Pom121L12',
'Por',
'Pparg',
'Prkaa1',
'Prkca',
'Pten',
'Ptgs2',
'Ptpn6',
'Pvt1',
'Qsox1',
'Rpl8',
'Sat1',
'Scp2',
'Slc11A2',
'Slc1A5',
'Slc25A28',
'Slc38A1',
'Slc39A14',
'Slc39A7',
'Smad7',
'Smg9',
'Snca',
'Snx4',
'Snx5',
'Socs1',
'Sting1',
'Tafazzin',
'Tbk1',
'Tfr2',
'Tgfb1',
'Tgfbr1',
'Timm9',
'Timp1',
'Tlr4',
'Tnfaip3',
'Tor2A',
'Trim21',
'Trim26',
'Trim46',
'Tsc1',
'Ttpa',
'Ulk1',
'Ulk2',
'Usp7',
'Wipi1',
'Wipi2',
'Wwtr1',
'Yap1',
'Ythdc2',
#'Yy1Ap1',
'Zeb1',
'Zfas1']
df = pd.DataFrame(columns=['Value', 'Average', 'Rate']) # 定义一个空的 DataFrame
# 读取数据有多少个
nras_expression = adata[adata.obs['Extract'] != 'Health'][:, check_list[1]].X
total_num = adata[adata.obs['Extract'] != 'Health'].X.shape[0]
print('表达数据的行数为:', total_num)
num_rows = adata[adata.obs['Extract'] != 'Health'].n_obs
# 打印行数
print('adata_Death_RNA 的行数为:', num_rows)
#读取adata中
num_rows_1 = adata[adata.obs['Extract'] == 'Health'].n_obs
# 打印行数
print('adata_Health_RNA 的行数为:', num_rows_1)
#读取adata中
# 循环遍历 check_list,将每个值保存到 DataFrame 中
for i, value in enumerate(check_list):
df.loc[i, 'Value'] = value # 只给 'Value' 列赋值
#取check_list中的Gene
Chosen_computing = check_list[i]
#print(Chosen_computing)
#取出这个基因对应的健康样本数目
#取列
select_index = adata.var.index == Chosen_computing
#取行
health_index = adata.obs['Extract'] == 'Health'
tarc_column = adata[health_index,select_index].X
# 提取非零元素并计算其数量
tarc_column_total = tarc_column.shape[0]
#print("Number of non-zero elements:", tarc_column)
#取出平均值
tarc_result = tarc_column.toarray()
tarc_mean = tarc_result.mean()
df.loc[i, 'Average'] = tarc_mean
#取出这个基因对应的疾病样本数
select_index = adata.var.index == Chosen_computing
#取行
death_index = adata.obs['Extract'] != 'Health'
death_tarc_column = adata[death_index,select_index].X
# 提取非零元素并计算其数量
death_tarc_column_total = death_tarc_column.shape[0]
#把要计算的基因样本抽出来
try:
compare_expression = adata[adata.obs['Extract'] != 'Health'][:, check_list[i]].X.toarray()
#print('compare_expression:',compare_expression )
average_standa = df.loc[i, 'Average']
#计算比较总数
count_number = np.sum(compare_expression > average_standa)
#count_number = sum(compare_expression >= df.loc[i, 'Average'])
#print('Sum:',count_number)
#计算比率
rate = count_number/death_tarc_column_total
except:
rate == 0
continue
#保存比率
df.loc[i, 'Rate'] = rate
# 打印最终的 DataFrame
print(df)
filename = "Check.csv"
file_path = os.path.join(result_folder, filename)
# Ensure the directory exists
os.makedirs(result_folder, exist_ok=True)
# Save the DataFrame to the specified CSV file
df.to_csv(file_path, index=False)
Result file saved at [LittleSnowFox's Anaconda installation directory]\database\Tracing_sample\Nerveferroptosis_19_21\result\.
