Mature Functions: Function Map of MI Tissue
1.Preprocessing
The default data file storage directory is C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE253768
Highly recommended to use Rstudio. Need to select the environment which containing anndata, in Tools > Global options > Python > Python interpreter
#File Structure
# ---[C:\]
# ---[GEOANALYSIS]
# ---[GSE232429]
# ---Sham1.csv
# ---Sham2.csv
# ---MI1.csv
# ---MI2.csv
1.1.Load required R packages (R)
# Load required packages
library(Seurat)
library(multtest)
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
library(patchwork)
library(tidyverse)
library(future)
library(harmony)
library(RColorBrewer)
1.2.Read file names and set the working directory (R)
# Create a vector to read files
setwd("C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE253768")
## Save the file names in the folder to 'dir_name'
dir_name <- list.files(pattern = "\\.csv$") # Match only CSV files
## View 'dir_name'
dir_name
#[1] "MI1.csv" "MI2.csv" "Sham1.csv" "Sham2.csv"
## Assign names to 'dir_name' (use file name without extension)
names(dir_name) <- gsub("\\.csv$", "", dir_name)
## View the renamed 'dir_name'
dir_name
## MI1 MI2 Sham1 Sham2
##"MI1.csv" "MI2.csv" "Sham1.csv" "Sham2.csv"
1.3.Batch read data and create Seurat objects (R)
## Batch data processing
scRNAlist <- list()
for (i in 1:length(dir_name)) {
# Read CSV file
counts <- read.csv(file = dir_name[i], row.names = 1) # Use the first column as row names
counts <- as.matrix(counts) # Convert to matrix format
# Create Seurat object and add file name as a label
scRNAlist[[i]] <- CreateSeuratObject(
counts = counts,
min.cells = 3,
min.features = 300,
project = names(dir_name)[i]
)
}
1.4.Calculate mitochondrial and red blood cell proportions (R)
# Check the Seurat object list
scRNAlist
# Calculate mitochondrial and red blood cell proportions in batch
for(i in 1:length(scRNAlist)){
sc <- scRNAlist[[i]]
# Calculate mitochondrial proportion
sc[["mt_percent"]] <- PercentageFeatureSet(sc, pattern = "^Mt-")
# Calculate red blood cell proportion
HB_genes <- c("Hba1","Hba2","Hbb","Hbd","Hbe1","Hbg1","Hbg2","Hbm","Hbq1","Hbz")
HB_m <- match(HB_genes, rownames(sc@assays$RNA))
HB_genes <- rownames(sc@assays$RNA)[HB_m]
HB_genes <- HB_genes[!is.na(HB_genes)]
sc[["HB_percent"]] <- PercentageFeatureSet(sc, features=HB_genes)
# Assign 'sc' back to scRNAlist[[i]]
scRNAlist[[i]] <- sc
# Remove 'sc'
rm(sc)
}
1.5.Quality control and preliminary merging (R)
# Perform a simple merge and then plot quality control (QC)
CI <- merge(scRNAlist[[1]], y=c(scRNAlist[[2]], scRNAlist[[3]], scRNAlist[[4]]))
head(colnames(CI))
unique(sapply(X = strsplit(colnames(CI), split = "_"), FUN = "[", 1))
plot1 <- FeatureScatter(CI, feature1 = "nFeature_RNA", feature2 = "mt_percent")
plot2 <- FeatureScatter(CI, feature1 = "nCount_RNA", feature2 = "nFeature_RNA")
CombinePlots(plots = list(plot1, plot2))# QC plot 1
VlnPlot(CI, features = c("mt_percent", "nFeature_RNA", "nCount_RNA", "HB_percent"), ncol = 4, pt.size=0)# QC plot 2
VlnPlot(CI, features = c("mt_percent", "nFeature_RNA", "nCount_RNA", "HB_percent"), ncol = 4, pt.size=0.5)# QC plot 3
1.6.Filter cells (R)
# Filter cells in batch
scRNAlist <- lapply(X = scRNAlist, FUN = function(x){
x <- subset(x,
subset = nFeature_RNA > 200 & nFeature_RNA < 5000 &
mt_percent < 10 &
HB_percent < 5 &
nCount_RNA < quantile(nCount_RNA,0.97))})
1.7.Data normalization, feature selection, and dimensionality reduction (R)
# Merge Seurat objects
scRNAlist <- merge(scRNAlist[[1]], y=c(scRNAlist[[2]], scRNAlist[[3]], scRNAlist[[4]]))
# Select highly variable genes and perform dimensionality reduction
scRNAlist <- NormalizeData(scRNAlist) %>%
FindVariableFeatures(selection.method = "vst",nfeatures = 3000) %>%
ScaleData() %>%
RunPCA(npcs = 30, verbose = T)
1.8.Harmony integration analysis (R)
# Integrate using Harmony
testAB.integrated <- RunHarmony(scRNAlist, group.by.vars = "orig.ident")
# Copy 'orig.ident' to 'Sample'
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Sample <- testAB.integrated@meta.data$orig.ident
# Copy 'orig.ident' to 'Group' and remove numbers
testAB.integrated@meta.data$Group <- gsub("[0-9]", "", testAB.integrated@meta.data$orig.ident)
1.9.Clustering and dimensionality reduction visualization (R)
# Check the updated metadata
head(testAB.integrated@meta.data)
# Add grouping information after integration
metadata <- testAB.integrated@meta.data
write.csv(metadata, file="meta.data.csv")# Export and save
#testAB.integrated@meta.data <- metadata
# Perform clustering
testAB.integrated <- FindNeighbors(testAB.integrated, reduction = "harmony", dims = 1:15) %>% FindClusters(resolution = 0.18)#15群
# Perform UMAP/tSNE dimensionality reduction
testAB.integrated <- RunTSNE(testAB.integrated, reduction = "harmony", dims = 1:15)
testAB.integrated <- RunUMAP(testAB.integrated, reduction = "harmony", dims = 1:25)
# Save
save(testAB.integrated, metadata, file = "MI Cell-15 clusters.Rdata")
# Export markers
testAB.integrated <- JoinLayers(testAB.integrated)
CI.markers <- FindAllMarkers(testAB.integrated, only.pos = TRUE, min.pct = 0.25, logfc.threshold = 0.25)
write.csv(CI.markers, file="MI Cell marker.csv")
1.10.Annotation and cluster labeling (R)
# Naming the 15 clusters
new.cluster.ids <- c("Fibroblasts", "Cardiomyocytes", "Endothelial cells",
"Cardiomyocytes", "Smooth muscle cells", "Macrophages",
"T cells", "Endothelial cells", "Endothelial cells",
"Mesothelial cells", "Macrophages", "Endothelial cells",
"Schwann cells", "Myofibroblast", "Endothelial cells")
names(new.cluster.ids) <- levels(testAB.integrated)
testAB.integrated <- RenameIdents(testAB.integrated, new.cluster.ids)
testAB.integrated$clusters2 <- testAB.integrated@active.ident
save(testAB.integrated, metadata, file = "MI Cell-15 clusters.Rdata")
1.11.Export results and visualization (R)
# Export the count of each cluster
Table1 <- table(testAB.integrated$Group, testAB.integrated$clusters2)
Table2 <- table(testAB.integrated$Sample, testAB.integrated$clusters2)
write.table(Table1, file = "Cell counts in each group.txt", sep ="\t")
write.table(Table2, file = "Cell counts in each sample.txt", sep ="\t")
# Export UMAP images from preliminary analysis
cell_type_cols <- c("#B383B9", "#F5CFE4","#EE934E","#F5D2A8","#fced82","#D2EBC8","#7DBFA7","#AECDE1","#3c77af")
p1 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", group.by = "clusters2", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Preliminary grouping of MI - overall.pdf", plot = p1, device = 'pdf', width = 21, height = 18, units = 'cm')
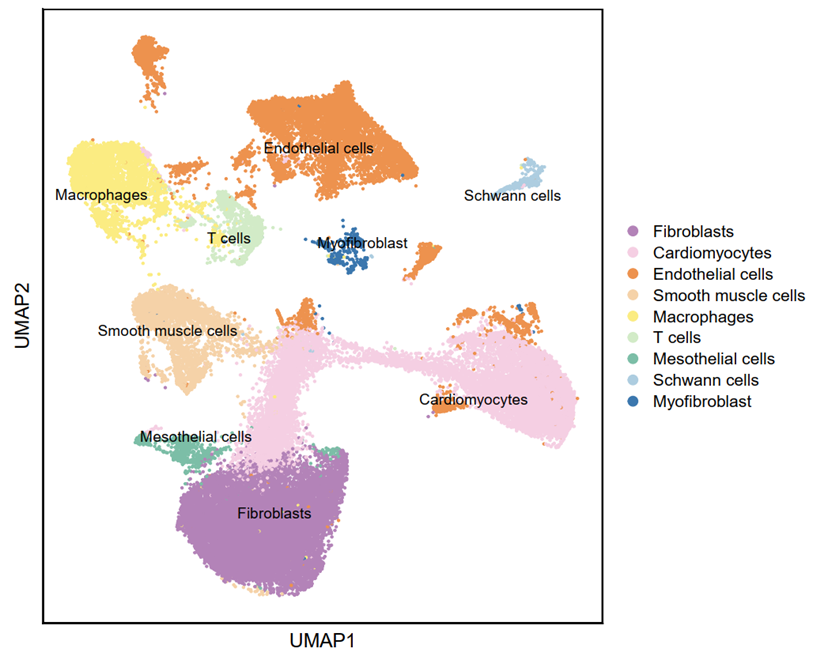
1.12.Generate the UMAP Plot (R)
p2 <- DimPlot(testAB.integrated, reduction = "umap", split.by = "Group", group.by = "clusters2", pt.size=0.5, label = T,repel = TRUE, raster=FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme(panel.border = element_rect(fill=NA,color="black", size=1, linetype="solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "Preliminary grouping of MI - split by group.pdf", plot = p2, device = 'pdf', width = 38, height = 18, units = 'cm')
2.Perform mixed analysis of the common transcriptome
2.1.Prepare the single-cell maps needed for use.
2.1.1.Save .h5ad (R)
#Removal of fibroblasts for storage
testAB.integrated <- subset(testAB.integrated,idents=c("Fibroblasts","Myofibroblast"),invert = FALSE)
testAB.integrated$RNA_snn_res.0.18 <- NULL
testAB.integrated$clusters1 <- NULL
testAB.integrated$clusters2 <- NULL
testAB.integrated$seurat_clusters <- NULL
#Re-finding highly variable genes
testAB.integrated <- NormalizeData(testAB.integrated) %>%
FindVariableFeatures(selection.method = "vst",nfeatures = 3000) %>%
ScaleData() %>%
RunPCA(npcs = 30, verbose = T)
#save
save(testAB.integrated, file = "MI-FibroblastCell.Rdata")
###Make sure the default gene is from RNA
DefaultAssay(testAB.integrated) <- "RNA"
testAB.integrated[["RNA"]] <- as(object = testAB.integrated[["RNA"]], Class = "Assay")#转成版本4的矩阵
###Make sure you select the matrix that contains all genes.
sceasy::convertFormat(
testAB.integrated,
from = "seurat",
to = "anndata",
outFile = "fibroblasts_allgene.h5ad"
)
Save the R variable table as variables.Rdata.
2.1.2.Run similarity (Python)
Move C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE253768/fibroblasts_allgene.h5ad to [Path of LittleSnowFox]/database/Clustering_sample/fibroblasts/data/
import numpy as np
import os
import LittleSnowFox as kl
#import matlab.engine
#eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab()
print(kl.__version__)
#初始化函数,将kailin转至工作目录。如果此前初始化过,那么在再次运行def kl_initialize(0)时,
#则拒绝初始化,避免套娃。运行def kl_initialize(1)时,强制重新初始化。
kl.kl_initialize(0)
#获取kailin工作的根目录
parent_directory_origin = kl.kl_settings.parent_directory_origin
#改进:
#添加一个cluster模式
#选择进行Lineage Tracing还是Cluster,并给出可用的列表
current_folder = kl.workcatalogue.choosemode_kl(parent_directory_origin,'Clustering',1)
h5ad_filename = "fibroblasts_allgene.h5ad"
file_name = "Sampling_Full_Base_8000.h5ad"
sample_choose = 'fibroblasts'
num_samples = 8000
current_folder_filter = os.path.join(current_folder, sample_choose)
current_folder_filter_1 = os.path.join(current_folder_filter, 'data')
filter_sample = os.path.join(current_folder_filter_1, h5ad_filename)
print(filter_sample)
import anndata
adata_filter = anndata.read_h5ad(filter_sample)
total_samples = adata_filter.shape[0]
if num_samples > total_samples:
raise ValueError(f"Requested {num_samples} samples, but only {total_samples} available.")
random_indices = np.random.choice(total_samples, num_samples, replace=False)
# 根据索引过滤数据
adata_random_subset = adata_filter[random_indices, :]
# 打印选取后的数据维度
print(f"Subset data shape: {adata_random_subset.shape}")
print(adata_random_subset)
print(current_folder_filter_1)
file_path = os.path.join(current_folder_filter_1, file_name)
adata_random_subset.write(file_path)
adata_random_subset
import numpy as np
import os
import LittleSnowFox as kl
#import matlab.engine
#eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab()
print(kl.__version__)
#初始化函数,将kailin转至工作目录。如果此前初始化过,那么在再次运行def kl_initialize(0)时,
#则拒绝初始化,避免套娃。运行def kl_initialize(1)时,强制重新初始化。
kl.kl_initialize(0)
#获取kailin工作的根目录
parent_directory_origin = kl.kl_settings.parent_directory_origin
#改进:
#添加一个cluster模式
#选择进行Lineage Tracing还是Cluster,并给出可用的列表
current_folder = kl.workcatalogue.choosemode_kl(parent_directory_origin,'Clustering',1)
h5ad_filename = "Sampling_Full_Base_8000.h5ad" #心梗-成纤维细胞-所有基因.h5ad
csv_filename = "tissue.csv" #心梗-成纤维细胞-所有基因.h5ad
sample_choose = 'fibroblasts'
num_samples = 8000
adata_merged = kl.preprocessing.merge_tissue_with_singlecell(
current_folder,
h5ad_filename,
csv_filename,
sample_choose,
num_samples
)
file_name = "adata_merged.h5ad"
file_path = os.path.join(current_folder_filter_1, file_name)
file_path
adata_merged.write(file_path)
2.2.Projecting organizations onto a single-cell functional map, calculate the cell similarity of the whole genome.(Python)
#选择要使用哪个样本
choosen_sample = "fibroblasts"
#选择.h5ad文件
h5ad_filename = "adata_merged.h5ad"
#运行自带的示例,并获取稀疏矩阵
#这里需要做非示例的函数进去
current_folder_input = current_folder
orig_adata,loading_directory,distance_matrix = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix(choosen_sample,h5ad_filename,"draw",current_folder_input,1,13000,0.1,0.001,True)
#orig_adata,loading_directory,distance_matrix_sparse = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix_sample(choosen_sample,h5ad_filename,"draw",current_folder_input)
#运行自带的示例,并获取非稀疏矩阵
#这里需要做非示例的函数进去
#current_folder_input = current_folder
#loading_directory,distance_matrix = kl.preprocessing.kl_dense_matrix(choosen_sample,h5ad_filename,"draw",current_folder_input)
print(loading_directory)
print(choosen_sample)
import os
import scipy.io
current_folder_result = os.path.join(loading_directory, 'result')
print(current_folder_result)
mat_name = "distance_matrix_merged.mat"
mat_path = os.path.join(current_folder_result, mat_name)
scipy.io.savemat(mat_path, {"distance_matrix": distance_matrix})
print(f"Distance matrix saved as MAT file to: {file_path}")
import pandas as pd
obs_names_list = orig_adata.obs_names.tolist()
var_names_list = orig_adata.var_names.tolist()
index = orig_adata.obs.index
df_orig_adata = pd.DataFrame({
"Index": index,
})
print(df_orig_adata)
csv_name = "orig_ident_merged.csv"
csv_path = os.path.join(current_folder_result, csv_name)
print(csv_path)
df_orig_adata.to_csv(csv_path, index=False)
2.3.Unsupervised learning (matlab)
The matlab file is located in [LittleSnowFox package]\database\Clustering_sample\fibroblasts\main_v3_matlab_run_me_merged_tissue.m
%% Load data and Split to compute
%% Load data and Split to compute
MM0 = load('./result/distance_matrix_merged.mat');
MM0 = MM0.distance_matrix;
%% 读取要排序的对象
count_=readtable('./result/orig_ident_merged.csv');
%% 得到边界划分点
%[p,splitlist] = binary_corr_sorting(MM0,20,125,5,5);
[p,splitlist] = binary_corr_sorting(MM0,20,200,5,5);
%% 对划分点去重
[uniqueList, ~, ~] = unique(splitlist, 'stable');
%% 对相似度矩阵排序
MM=MM0(p,p);
split=[];
%% 重排count_result
count_result=count_(p,:);
split_simple=uniqueList;
%% 第一个起始位点置为1
split_simple(1)=1;
split_simple=[split_simple,length(MM0)];
%% 计算均值矩阵
[simple_matrix]=sample_computing(count_result,split_simple,MM,"mean");
%% 合并成小矩阵
ClusterReslut=cluster_map(split_simple,simple_matrix,0,0.0002,0);
count_result.Result = ClusterReslut;
%重排小矩阵
[cluster_map_matrix] = genetic_encoder( ...
simple_matrix, ...
60, ...% nPop = 50; % 种群规模大小为30
1, ...% nPc = 1; % 子代规模的比例0.8
200, ...% maxIt = 200; % 最大迭代次数
5 ...% cycletimes = 200; % 循环计算次数
);
%重拍小矩阵方案2
% 创建行和列标签(示例)
%row_labels = cluster_map_label;
%column_labels = cluster_map_label;
% 使用 heatmap 函数并传递相应参数
h = heatmap(cluster_map_matrix);
%h.YDisplayLabels = row_labels; % 设置行标签
%h.XDisplayLabels = column_labels; % 设置列标签
h.ColorLimits = [0,0.0002]%
%% 临近法激活
corr_matrix = relevance_generate(0.0002,2,cluster_map_matrix);
hi = heatmap(corr_matrix);
%% 编码
encode_result = encoder_corr_matrix(0.000201,0.000199,10,2,cluster_map_matrix);
figure(2)
hj = heatmap(encode_result);
%% 解码
figure(3)
[weighting_decode,decode_result] = decoder_corr_matrix(encode_result);
weighting_result = decode_result;
hk = heatmap(weighting_result);
hk.ColorLimits = [33,34]
writetable(count_result, './result/result_merged.csv');
3.Perform the mapping from tissue to single cells. (R)
Read the R variable table as variables.Rdata.
Move adata_merged.h5ad from [LittleSnowFox installation path]\database\Clustering_sample\fibroblasts\data\adata_merged.h5ad to C:\GEOANALYSIS\GSE253768\
Move result_merged.csv from [LittleSnowFox installation path]\database\Clustering_sample\fibroblasts\data\result_merged.csv to C:\GEOANALYSIS\GSE253768\
library(SeuratDisk)
# Set the input file path and output file path
input_file <- "adata_merged.h5ad" # Replace with your h5ad file path
output_file <- "adata_merged.h5seurat" # Convert to temporary h5seurat file
# Convert .h5ad to .h5seurat format
Convert(input_file, dest = "h5seurat", overwrite = TRUE)
# Load .h5seurat file to Seurat object
seurat_object <- LoadH5Seurat(output_file)
# View Seurat object information
print(seurat_object)
## Regenerate meta.data
load("C:/GEOANALYSIS/GSE253768/MI-FibroblastCell.Rdata")
# Extract meta.data of testAB.integrated and seurat_object
meta_testAB <- testAB.integrated@meta.data
meta_seurat <- seurat_object@meta.data
# Extract "orig.ident", "Group", "Sample" from testAB.integrated
selected_metadata <- meta_testAB[, c("orig.ident", "Group", "Sample")]
# Ensure row names are aligned
rownames(selected_metadata) <- rownames(meta_testAB)
# Initialize new metadata for seurat_object
meta_seurat$orig.ident <- NA
meta_seurat$Group <- NA
meta_seurat$Sample <- NA
# Align metadata from testAB.integrated to seurat_object
common_cells <- intersect(rownames(meta_seurat), rownames(selected_metadata))
meta_seurat[common_cells, c("orig.ident", "Group", "Sample")] <- selected_metadata[common_cells, ]
# Add new labels for extra cells in seurat_object
additional_cells <- setdiff(rownames(meta_seurat), rownames(selected_metadata))
# Set new Group and Sample names
meta_seurat[additional_cells, "orig.ident"] <- additional_cells # Set orig.ident as the cell label
meta_seurat[additional_cells, "Group"] <- additional_cells # Set Group as the cell label
meta_seurat[additional_cells, "Sample"] <- additional_cells # Set Sample as the cell label
# Update meta.data of seurat_object
seurat_object@meta.data <- meta_seurat
# View the updated meta.data
head(seurat_object@meta.data)
##Import the new grouping results
#index_result <- read.csv("result_merged.csv")
# Load the dataset
data <- read.csv("result_merged.csv")
# Modify the Var1 column
data$Var1 <- paste(data$Var1, data$Var2, sep = "_")
# Set Var1 as row names and remove the Var1 column
rownames(data) <- data$Var1
data <- data[ , !(names(data) %in% "Var1")]
index_result <- data
##Make sure the table's Index is consistent with the Cell name of the Seurat object
##Set the Index as the row name to facilitate subsequent operations
#rownames(index_result) <- index_result$Var1
##Match the Result column to the metadata of the Seurat object according to the Index
metadata <- seurat_object@meta.data # Get the metadata of the Seurat object
metadata$Result <- index_result[rownames(metadata), "Result"]
##Update the metadata of the Seurat object
seurat_object@meta.data <- metadata
##Check the updated metadata
head(seurat_object@meta.data)
#Add Fenqun3
#Specify Cell grouping
mi_cells <- c("MI.1", "MI.2", "MI.3", "MI.4")
#Update the meta.data of the Seurat object and create a new Fenqun3 column
seurat_object@meta.data <- seurat_object@meta.data %>%
mutate(Fenqun4 = case_when(
orig.ident %in% mi_cells ~ "MI",
Result >= 1 & Result <= 9 ~ "FibR2-G1",
Result >= 10 & Result <= 12 ~ "FibR2-G2",
Result >= 13 & Result <= 25 ~ "FibR2-G3",
Result >= 26 & Result <= 33 ~ "FibR2-G4",
Result >= 34 & Result <= 41 ~ "FibR2-G5",
Result >= 42 & Result <= 50 ~ "FibR2-G6",
Result >= 51 & Result <= 59 ~ "FibR2-G7",
TRUE ~ NA_character_
))
# View updated meta.data
head(seurat_object@meta.data)
# Redraw UMAP
seurat_object <- SCTransform(seurat_object,assay = 'RNA')
seurat_object <- RunPCA(seurat_object)
ElbowPlot(seurat_object)
seurat_object <- RunUMAP(seurat_object, dims = 1:10)
## Make a plot highlighting MI and Sham
# Create a new column Fenqun3's UMAP plot
cell_type_cols <- c("#ffffcc","#5a5098","#a3caa9","#deedad","#bd5c56","#efd695","#dd9667","#6693b1","#842844")
# Create a new column to define the point size based on the "Fenqun4" column
seurat_object@meta.data$point_size <- ifelse(seurat_object@meta.data$Fenqun4 %in% c("MI"), 3, 0.1)
# Use DimPlot to make a UMAP plot, keeping the original colors and labels, but resizing the points
p1 <- DimPlot(seurat_object, reduction = "umap", group.by = "Fenqun4", pt.size = seurat_object@meta.data$point_size, label = TRUE, repel = TRUE, raster = FALSE, cols = cell_type_cols) + labs(x = "UMAP1", y = "UMAP2") + theme( panel.border = element_rect(fill = NA, color = "black", size = 1, linetype = "solid"), axis.text.y = element_blank(), axis.ticks.y = element_blank(), axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
ggsave(filename = "UMAP diagram highlighting MI and Sham points.pdf", plot = p1, device = 'pdf', width = 21, height = 18, units = 'cm')
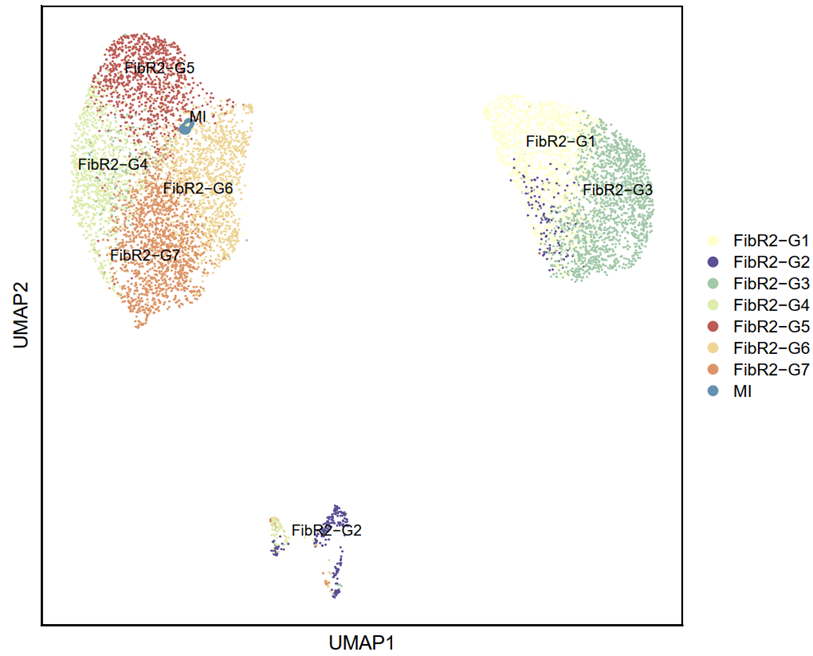
4.Save the result (R)
save(seurat_object, file = "MI-FibroblastCell-mixed with whole transcriptome data.Rdata")
# Export markers
Idents(seurat_object) <- "Fenqun"
CI.markers <- FindAllMarkers(seurat_object, only.pos = TRUE, min.pct = 0.25, logfc.threshold = 0.25)
write.csv(CI.markers, file="8000 Cells mixed with normal transcriptome markers.csv")
